Banque de France Bulletin no. 239: Article 6 Technological change and outsourcing: an illustration through broadband Internet access in France
The work organisation in companies is increasingly “fragmented” due to the growing use of outsourcing of activities that are not considered as “core business”. Outsourcing is the process whereby a company separates itself from an activity that was previously carried out in-house and allocates it to a specialized external service company. This article summarises a recent study (Bergeaud et al., 2021) conducted at the Banque de France on the role of technological change in the outsourcing process. The authors study the impact of broadband Internet access in France between 1999 and 2007 on the work organization in companies and on workers. They conclude that this technological shock triggered a reorganization of companies and contributed to the rise of outsourcing. For workers directly affected by this outsourcing process, the impact on wages depends on their level of technical qualification.
1 The context: fragmentation of work organisation and technological change
Outsourcing is the process whereby a company separates itself from an activity that was previously carried out in house and allocates it to a specialized external service company. This is particularly the case for activities considered to be peripheral and which are entrusted to outsourcing partners which offer similar services with greater flexibility. The activities traditionally concerned correspond to support functions, as diverse as IT, human resources, accounting, marketing, communication, security and cleaning. The company can thus restructure and focus on its core competences: its “core business”, i.e. the activities directly concerned by its production process.
Recent academic work on European companies emphasizes the development of the fragmentation of work organization in Europe. In France, Le Moigne (2020) shows that support functions are less and less carried out in house and are often entrusted to external service companies, which suggests strong reorganisations within companies. In the United Kingdom, Aghion et al. (2019) show a link between the outsourcing of activities, such as cleaning and security, and corporate productivity. Finally, Goldschmidt and Schmieder (2017) analyse the process of fragmentation of work organisation in Germany, where companies increasingly have recourse to service companies, temporary employment agencies and external service companies rather than hire employees.
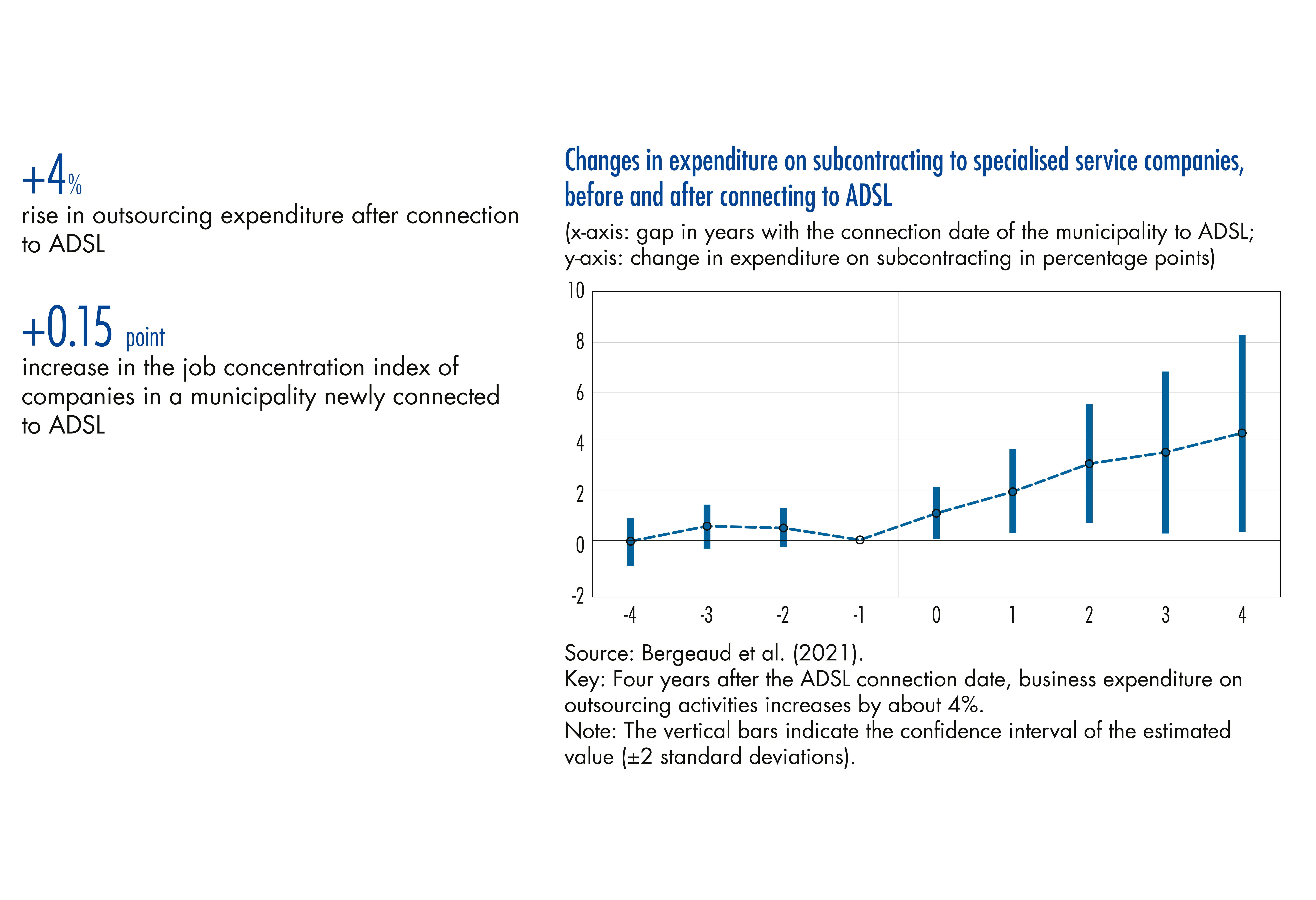
One of the determinants of this fragmentation process in the workplace could be technological change (Weil, 2017): new information and communication technologies offer many possibilities for coordinating and controlling work inside and outside the company. In this article, we present the results of a recent article (Bergeaud et al., 2021), in which the authors test this hypothesis by studying the effect of technological change on the outsourcing decision, and the consequences for workers. To this end, they mobilise a large scale technological shock: the gradual roll out of broadband Internet (via ADSL) in France, from 1999 to 2007.
A technological shock: the development of ADSL in France
France Telecom launched ADSL commercially in 1999. Thanks to this technology, it is possible to use the pre existing telephone network to transmit digital data. Its roll out was very gradual: the major urban centres were equipped from the early 2000s, while rural and remote areas were not equipped until ten years later (see Chart 1). One of the reasons for this gradual roll out is the eligibility of telephone network for this new technology. …
Download the PDF version of this document

- Published on 04/14/2022
- 8 pages
- EN
- PDF (16.58 MB)
Bulletin Banque de France 239
Updated on: 04/14/2022 10:16